Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics of Conductivity
Conductivity meters are essential tools used in various industries to measure the ability of a solution to conduct electricity. Understanding how to use a conductivity meter is crucial for obtaining accurate and reliable results. In this article, we will discuss the basics of conductivity and provide a step-by-step guide on how to use a conductivity meter effectively.
Conductivity is a measure of the ability of a solution to conduct electricity. It is influenced by the concentration of ions in the solution, as well as the temperature of the solution. Solutions with a high concentration of ions will have a higher conductivity, while solutions with a low concentration of ions will have a lower conductivity. Temperature also plays a role in conductivity, as higher temperatures can increase the mobility of ions in the solution, leading to higher conductivity.
To measure the conductivity of a solution, a conductivity meter is used. A conductivity meter consists of a probe that is immersed in the solution and connected to a meter that displays the conductivity value. Before using a conductivity meter, it is important to calibrate the meter to ensure accurate measurements. Calibration involves adjusting the meter to a known standard solution with a specific conductivity value.
To use a conductivity meter, start by preparing the solution to be tested. Ensure that the solution is at room temperature, as temperature can affect conductivity measurements. Next, turn on the conductivity meter and allow it to warm up for a few minutes. Immerse the probe of the conductivity meter into the solution, making sure that the probe is fully submerged and not touching the sides of the container.
Once the probe is immersed in the solution, wait for the meter to stabilize and display a reading. The conductivity value will be displayed in units of Siemens per centimeter (S/cm) or microsiemens per centimeter (\u00b5S/cm). Record the conductivity value and compare it to the expected conductivity of the solution. If the measured conductivity is significantly different from the expected value, recalibrate the meter and repeat the measurement.
| Product name | pH/ORP-8500A transmitter controller | ||
| Measurement parameter | Measurement Range | Resolution ratio | Accuracy |
| pH | 0.00\uff5e14.00 | 0.01 | \u00b10.1 |
| ORP | (-1999\uff5e+1999)mV | 1mV | \u00b15mV(Electric meter) |
| Temperature | (0.0\uff5e100.0)\u2103 | 0.1\u2103 | \u00b10.5\u2103 |
| Temperature range of Tested solution | (0.0\uff5e100.0)\u2103 | ||
| Temperature component | NTC10K thermal element | ||
| (4~20)mA Current output | Channel No. | 2 channels | |
| Technical characteristics | Isolated, fully adjustable, reverse, | ||
| configurable, instrument / transmitting dual mode | |||
| Loop resistance | 400\u03a9(Max)\uff0cDC 24V | ||
| Transmission accuracy | \u00b10.1mA | ||
| Control contact | Channel NO. | 3 Channels | |
| Electric contact | Semiconductor photoelectric switch | ||
| Programmable | Each channel can be programmed and point to (temperature, pH/ORP, time) | ||
| Technical characteristics | Presetting of normally open /normally closed state / pulse /PID regulation | ||
| Load capacity | 50mA(Max)AC/DC 30V | ||
| Data\u00a0communication | MODBUS, RS485 standard protocol | ||
| Working power supply | DC 24V\u00b14V | ||
| Overall power consumption | \uff1c5.5W | ||
| Working Environment | Temperature: (0~50) \u2103 | ||
| Relative humidity: \u2264 85%RH (non condensing) | |||
| Storage environment | Temperature: (-20~60) \u2103 | ||
| Relative humidity: \u2264 85%RH (non condensing) | |||
| Protection level | IP65 (with back cover) | ||
| Shape size | 96mm\u00d796 mm\u00d794mm (H\u00d7W\u00d7D) | ||
| Opening size | 91mm\u00d791mm(H\u00d7W) | ||
| Fixed mode | Panel mounting type quick fixed | ||
When using a conductivity meter, it is important to handle the probe with care to avoid damaging it. Avoid touching the probe with bare hands, as oils and dirt from the skin can affect conductivity measurements. Rinse the probe with deionized water before and after each use to ensure accurate measurements.
In addition to measuring conductivity, conductivity meters can also be used to monitor the purity of water in various industries, such as pharmaceuticals, Food And Beverage, and environmental monitoring. Conductivity meters are also used in research laboratories to study the behavior of ions in solutions and to monitor chemical reactions.
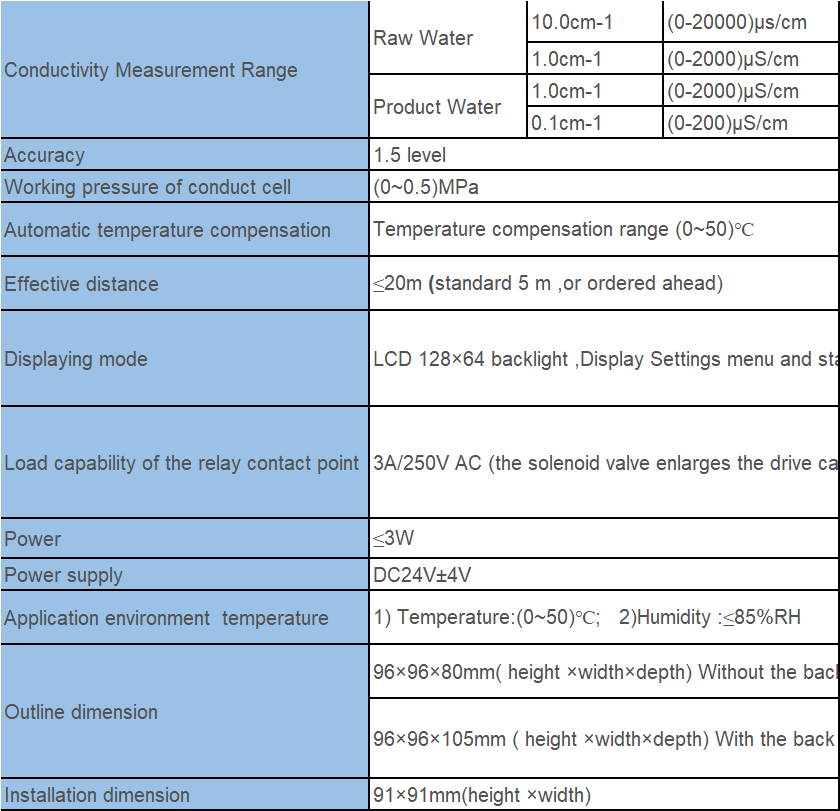
In conclusion, conductivity meters are valuable tools for measuring the conductivity of solutions and monitoring water purity in various industries. By understanding the basics of conductivity and following the proper steps for using a conductivity meter, accurate and reliable measurements can be obtained. Remember to calibrate the meter before use, handle the probe with care, and ensure that the solution is at the correct temperature for accurate measurements. With practice and attention to detail, using a conductivity meter can be a straightforward and effective process.

