Table of Contents
Chủ đề blog: Khám phá vai trò của máy biến áp phụ trợ trong phân phối điện
Máy biến áp phụ trợ đóng vai trò quan trọng trong hệ thống phân phối điện, đóng vai trò là thành phần quan trọng trong việc đảm bảo truyền tải điện hiệu quả và đáng tin cậy. Những máy biến áp này được thiết kế để giảm điện áp từ nguồn điện chính xuống mức phù hợp để phân phối cho gia đình, doanh nghiệp và những người dùng cuối khác. Trong bài viết này, chúng ta sẽ khám phá tầm quan trọng của máy biến áp phụ trợ trong phân phối điện và thảo luận về các đặc điểm chính khiến chúng trở nên cần thiết trong các hệ thống điện hiện đại.
Một trong những chức năng chính của máy biến áp phụ trợ là giảm điện áp của nguồn điện đang được sử dụng. truyền từ nguồn điện chính. Điều này là cần thiết vì điện áp do các nhà máy điện tạo ra thường quá cao để phân phối an toàn và hiệu quả. Bằng cách giảm điện áp xuống mức thấp hơn, máy biến áp phụ giúp truyền tải điện một cách an toàn trên khoảng cách xa mà không có nguy cơ quá nhiệt hoặc các vấn đề về điện khác.
Ngoài việc điều chỉnh điện áp, máy biến áp phụ còn đóng vai trò quan trọng trong việc cách ly các bộ phận khác nhau của hệ thống phân phối điện. Bằng cách cung cấp một rào chắn giữa đường dây truyền tải điện áp cao và đường dây phân phối điện áp thấp hơn, các máy biến áp này giúp ngăn ngừa sự đột biến điện và các nhiễu loạn điện khác ảnh hưởng đến người dùng cuối. Sự cách ly này cũng giúp phát hiện và giải quyết mọi vấn đề có thể phát sinh trong hệ thống dễ dàng hơn, đảm bảo rằng nguồn điện được phân phối một cách đáng tin cậy và nhất quán.
| mô hình | Định mức công suất (KVA) | Điện áp tổ hợp(KV) | Giảm tải tổn thất(W) | Tải tổn thất(W) | Giảm tải current ( phần trăm ) | Đoản mạch điện áp ( phần trăm ) |
| SC13-30 | 30 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 150 | 710 | 2.3 | 4.0 |
| SC13-50 | 50 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 215 | 1000 | 2.2 | 4.0 |
| SC13-80 | 80 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 295 | 1380 | 1.7 | 4.0 |
| SC13-100 | 100 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 320 | 1570 | 1.7 | 4.0 |
| SC13-125 | 125 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 375 | 1850 | 1.5 | 4.0 |
| SCB13-160 | 160 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 430 | 2130 | 1.5 | 4.0 |
| SCB13-200 | 200 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 495 | 2530 | 1.3 | 4.0 |
| SCB13-250 | 250 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 575 | 2760 | 1.3 | 4.0 |
| SCB13-315 | 315 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 705 | 3470 | 1.1 | 4.0 |
| SCB13-400 | 400 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 785 | 3990 | 1.1 | 4.0 |
| SCB13-500 | 500 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 930 | 4880 | 1.1 | 4.0 |
| SCB13-630 | 630 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 1070 | 5880 | 0.9 | 4.0 |
| SCB13-630 | 630 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 1040 | 5960 | 0.9 | 6.0 |
| SCB13-800 | 800 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 1210 | 6960 | 0.9 | 6.0 |
| SCB13-1000 | 1000 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 1410 | 8130 | 0.9 | 6.0 |
| SCB13-1250 | 1250 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 1670 | 9690 | 0.9 | 6.0 |
| SCB13-1600 | 1600 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 1960 | 11700 | 0.9 | 6.0 |
| SCB13-2000 | 2000 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 2440 | 14400 | 0.7 | 6.0 |
| SCB13-2500 | 2500 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 2880 | 17100 | 0.7 | 6.0 |
Một trong những đặc điểm chính giúp phân biệt máy biến áp phụ với các loại máy biến áp khác là việc sử dụng lõi thép silic định hướng cán nguội. Loại vật liệu lõi này có hiệu quả cao trong việc giảm tổn thất năng lượng và cải thiện hiệu suất tổng thể của máy biến áp. Bằng cách sử dụng lõi thép silic định hướng cán nguội, máy biến áp phụ có thể hoạt động ở mức hiệu suất cao hơn, giúp giảm chi phí năng lượng và giảm tác động đến môi trường.
Trung Quốc đã nổi lên như một nước xuất khẩu và sản xuất máy biến áp phụ trợ hàng đầu, với nhiều nhà sản xuất trong nước sản xuất máy biến áp chất lượng cao để sử dụng trong các hệ thống phân phối điện trên toàn thế giới. Những máy biến áp này nổi tiếng về độ tin cậy, độ bền và hiệu quả, khiến chúng trở thành lựa chọn phổ biến cho các công ty tiện ích và các tổ chức khác phụ thuộc vào nguồn cung cấp điện ổn định.
| Chuyển đổi khô | Công suất định mức (KVA) | Điện áp tổ hợp(KV) | Không tải tổn thất(W) | Tải tổn thất(W) | Không tải current ( phần trăm ) | Đoản mạch điện áp ( phần trăm ) |
| SC11-30 | 30 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 180 | 710 | 2.4 | 4.0 |
| SC11-50 | 50 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 250 | 1000 | 2.4 | 4.0 |
| SC11-80 | 80 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 340 | 1380 | 1.8 | 4.0 |
| SC11-100 | 100 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 360 | 1570 | 1.8 | 4.0 |
| SC11-125 | 125 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 420 | 1850 | 1.6 | 4.0 |
| SCB11-160 | 160 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 490 | 2130 | 1.6 | 4.0 |
| SCB11-200 | 200 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 560 | 2530 | 1.4 | 4.0 |
| SCB11-250 | 250 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 650 | 2760 | 1.4 | 4.0 |
| SCB11-315 | 315 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 790 | 3470 | 1.2 | 4.0 |
| SCB11-400 | 400 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 880 | 3990 | 1.2 | 4.0 |
| SCB11-500 | 500 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 1050 | 4880 | 1.2 | 4.0 |
| SCB11-630 | 630 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 1210 | 5880 | 1.0 | 4.0 |
| SCB11-630 | 630 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 1170 | 5960 | 1.0 | 6.0 |
| SCB11-800 | 800 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 1370 | 6960 | 1.0 | 6.0 |
| SCB11-1000 | 1000 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 1590 | 8130 | 1.0 | 6.0 |
| SCB11-1250 | 1250 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 1880 | 9690 | 1.0 | 6.0 |
| SCB11-1600 | 1600 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 2210 | 11730 | 1.0 | 6.0 |
| SCB11-2000 | 2000 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 2720 | 14450 | 0.8 | 6.0 |
| SCB11-2500 | 2500 | 6,6.3,6.6,10,11/0.4 | 3200 | 17170 | 0.8 | 6.0 |
Để tìm hiểu thêm về vai trò của máy biến áp phụ trong phân phối điện, có một số video thông tin trực tuyến cung cấp giải thích chi tiết về cách thức hoạt động của các máy biến áp này và lý do tại sao chúng lại cần thiết trong hệ thống điện hiện đại. Những video này cung cấp nguồn tài liệu quý giá cho bất kỳ ai muốn hiểu rõ hơn về tầm quan trọng của máy biến áp phụ trợ trong việc truyền tải và phân phối điện.
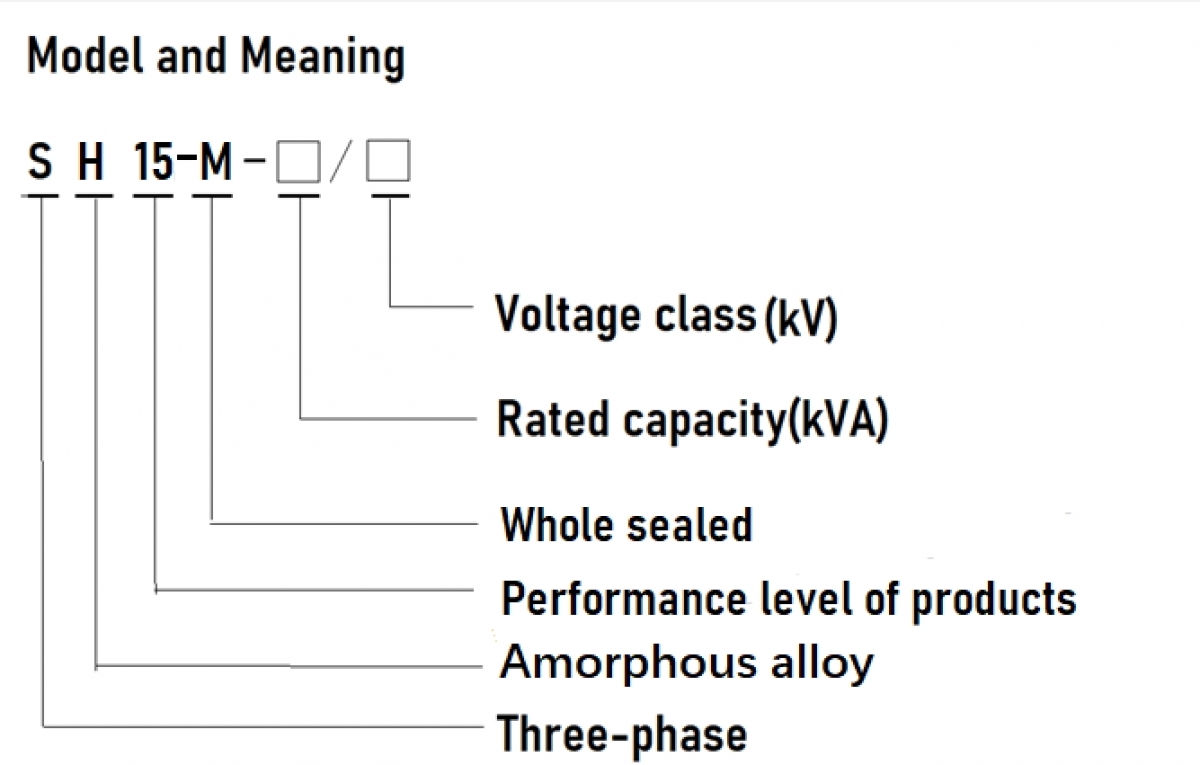
Tóm lại, máy biến áp phụ đóng vai trò quan trọng trong hệ thống phân phối điện, giúp điều chỉnh điện áp, cách ly các bộ phận khác nhau của hệ thống và nâng cao hiệu suất tổng thể. Với việc sử dụng lõi thép silicon định hướng cán nguội và các tính năng tiên tiến khác, những máy biến áp này rất cần thiết để đảm bảo truyền tải điện hiệu quả và đáng tin cậy đến người dùng cuối. Khi Trung Quốc tiếp tục dẫn đầu trong việc sản xuất máy biến áp phụ chất lượng cao, rõ ràng những thiết bị này sẽ vẫn là thành phần chính của hệ thống điện hiện đại trong nhiều năm tới.

